Overview
In today’s digital age, where data flows like the lifeblood of businesses, institutions, and homes, selecting the right network cabling is as crucial as laying the foundation for a modern city. As we venture through the ever-evolving technology landscape of 2023, the world of networking and cabling takes center stage. Our very connected existence hinges on this choice.
This blog serves as your guide, navigating you through the intricate world of networking decisions. We’ll explore the paramount choice that network administrators, business owners, and tech-savvy homeowners must make: deciding between fiber optic cabling and Cat6 cabling. We’ll uncover the benefits, applications, and considerations for both of these networking stalwarts, shedding light on the paths they carve in 2023.
In an era where the Internet of Things (IoT) knits together a tapestry of interconnected devices, where remote work isn’t a luxury but a necessity, and where the digital realm spins ever faster, your network infrastructure becomes your digital pulse. With this context, we embark on our journey to unveil the essence of networking in 2023 and the choices that will shape your connectivity landscape.
What is Fiber Optic Cabling?
Fiber optic cabling, often called “fiber,” employs thin glass or plastic strands to transmit data as light signals. Encased in protective layers, these optical fibers enable high-speed data transmission over extended distances.

Pros of Fiber Optic Cabling:
- High Data Transfer Speeds: Fiber optic cabling is renowned for its exceptional data transfer speeds, operating at the speed of light, far surpassing traditional copper cables.
- Immunity to Interference: Fiber optics remain immune to electromagnetic and radio frequency interference, ideal for environments with high EMI/RFI levels.
- Long Transmission Distances: They excel in transmitting data over considerable distances without signal degradation, making them suitable for long-haul telecommunications.
- Security: Fiber optic signals are highly secure, as they are challenging to intercept due to a lack of electromagnetic signals.
- Low Latency: Low latency is crucial for real-time applications, and fiber optic cabling delivers in spades, benefiting activities like video conferencing and online gaming.
- Thin and Lightweight: Fiber cables are thinner and lighter than copper cables, simplifying installation in tight spaces.
- Future-Proofing: Fiber optic cabling is poised to meet the demands of increasing data and emerging technologies for years to come.
Cons of Fiber Optic Cabling:
- Cost: Fiber optic cabling is pricier, both in terms of cables and associated equipment, compared to traditional copper cabling.
- Fragility: Fiber optic cables are delicate and require careful handling during installation and maintenance.
- Installation Complexity: Specialized knowledge and equipment may be necessary for installation.
- Limited Compatibility: Not always directly compatible with legacy systems and may require adapters or converters.
- Maintenance Challenges: Troubleshooting and repairs can be complex, necessitating specialized tools and expertise.
Despite these drawbacks, the advantages of fiber optic cabling, such as speed and security, make it a preferred choice for high-performance networking and telecommunications applications, depending on specific needs and priorities.
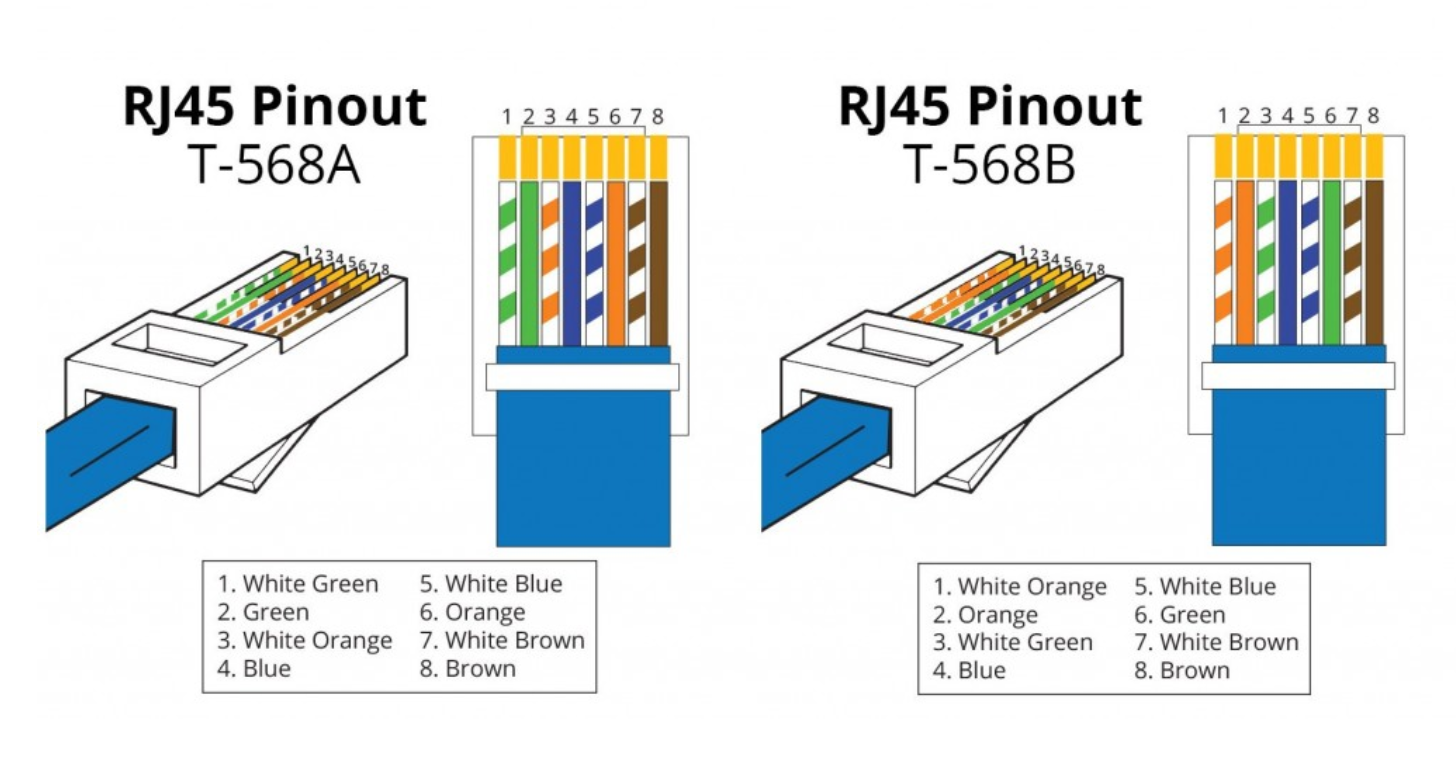
What is Cat6 Cabling?
Cat6, short for Category 6, is an Ethernet cable designed for networking and data transmission, surpassing its predecessor, Cat5e. It offers improved data speeds and reduced crosstalk.

Pros of Cat6 Cabling:
- Affordability: Cat6 is a cost-effective alternative to fiber optics, suitable for various networking needs.
- High Data Transfer Speeds: It supports Gigabit Ethernet and even 10 Gigabit Ethernet over shorter distances.
- Compatibility: Backward compatible with earlier Ethernet standards (Cat5, Cat5e), enabling gradual network upgrades.
- Ease of Installation: Cat6 cables are straightforward to install and terminate, making them practical for many scenarios.
- Flexibility: Available in various lengths, Cat6 cables accommodate diverse networking setups.
- Scalability: Cat6 cabling supports future network expansion and higher data rates.
Cons of Cat6 Cabling:
- Distance Limitations: High-speed data transfer is limited over longer distances, typically up to 55 meters for 10 Gigabit Ethernet.
- Interference: Cat6 is susceptible to interference, particularly in environments with high electromagnetic interference.
- Installation Quality: Performance is contingent on proper installation and termination.
- Future-Proofing: May not be ideal for ultra-high-speed or long-distance applications, which might necessitate Cat6a or fiber optics.
- Cost of Equipment: To fully utilize Cat6 capabilities, compatible networking equipment may be required.
Cat6 cabling is suitable for many networking scenarios, offering a balance between cost and performance. It’s commonly employed in small to medium-sized businesses, home networks, and educational institutions. The choice depends on specific networking requirements, budget, and potential for future growth.
What is the Differences Between Fiber Optic and Cat6 Cabling?

Transmission Medium:
Fiber Optic Cabling: Uses optical fibers to transmit data as light signals.
Cat6 Cabling: Relies on copper conductors to transmit electrical signals through twisted pairs of wires.
Data Transfer Speeds:
Fiber Optic Cabling: Offers significantly higher data transfer speeds, supporting Gigabit, 10 Gigabit, 40 Gigabit, and even 100 Gigabit Ethernet.
Cat6 Cabling: Designed for high-speed data transfer, typically limited to Gigabit Ethernet over longer distances, supporting 10 Gigabit Ethernet for shorter runs.
Immunity to Interference:
Fiber Optic Cabling: Immune to electromagnetic and radio frequency interference due to its use of light signals.
Cat6 Cabling: Susceptible to EMI and RFI, which can lead to signal degradation in noisy environments.
Distance Limitations:
Fiber Optic Cabling: Suitable for long-distance data transmission with minimal signal loss.
Cat6 Cabling: Limited distance for high-speed data transfer, especially over longer runs.
Installation and Maintenance:
Fiber Optic Cabling: Requires specialized tools and expertise, with delicate handling and potentially complex maintenance.
Cat6 Cabling: Easier to install and terminate, making it more practical for small to medium-sized networks, with relatively straightforward maintenance.
Cost:
Fiber Optic Cabling: Typically more expensive than Cat6, both in terms of cables and associated equipment.
Cat6 Cabling: More budget-friendly, often chosen for cost-conscious projects.
When to Choose Fiber Optic Cabling?
High Data Transfer Speeds: For networks requiring speeds beyond 1 Gbps, especially 10 Gigabit or faster, fiber optic cabling is ideal.
Long-Distance Connectivity: When spanning extended distances without signal degradation is necessary.
Resistance to Interference: In environments with high EMI/RFI, fiber optics provide reliable data transmission.
High Security Requirements: When data security is paramount due to its difficulty of interception.
Future-Proofing: As a solution capable of meeting increasing data demands and emerging technologies.
When Cat6 Cabling is More Suitable?
Budget Constraints: In cost-conscious projects with limited budgets.
Moderate Data Speed Requirements: For networks where speeds up to 1 Gbps suffice.
Ease of Installation: In scenarios where quick and straightforward installation is essential.
Scalability with Budget Constraints: For businesses expecting network expansion while keeping initial costs manageable.
Compatibility with Existing Infrastructure: When backward compatibility is needed to upgrade networks incrementally.
In conclusion, the choice between fiber optic and Cat6 cabling hinges on a thorough assessment of your specific network requirements. Factors like budget, data speed, distance, interference, and future growth must be considered to make an informed decision. Your choice not only meets current needs but also lays the foundation for your network’s future.
Future Trends and Considerations for Fiber Optic Cabling and Cat6 Cabling
In 2023 and beyond, the networking landscape evolves with emerging technologies and trends that impact the choice between fiber optic cabling and Cat6 cabling. These considerations include:
Demand for Higher Data Speeds: Emerging technologies, like 5G and IoT, drive the need for even faster data speeds. Fiber optics excel in scenarios requiring 10 Gigabit Ethernet or faster data rates, while Cat6 may suffice for moderate-speed applications.
5G and Edge Computing: The growth of 5G and edge computing necessitates robust and reliable network infrastructure. Fiber optics can meet high-speed, low-latency requirements for 5G and edge computing.
Data Center Upgrades: Data centers increasingly adopt 400 Gigabit and 800 Gigabit Ethernet standards, where fiber optic cabling, especially single-mode fiber, is essential for high-speed connections over long distances.
Fiber to the Home (FTTH): As more households seek high-speed internet, FTTH deployments rise, with fiber optic cabling delivering high-speed internet directly to homes.
Wireless Backhaul Networks: Fiber optics are vital for backhauling data from 5G small cells and wireless network infrastructure, providing necessary bandwidth and low latency.
Smart Cities and IoT: Smart cities and IoT growth heighten the demand for robust, high-speed networks. Fiber optic cabling supports these applications by delivering high data rates over long distances.
Environmental Considerations: Sustainability and reduced energy consumption become critical, with emerging cabling technologies aiming to minimize power usage. Fiber optics have an advantage due to their lower power requirements for data transmission.
New Fiber Optic Standards: Emerging standards push the boundaries of speed and reach, making fiber optic cabling even more versatile and future-proof.
Cat6a and Beyond: Cat6a may remain practical for businesses seeking cost-effective solutions between Cat6 and fiber.
Hybrid Solutions: Combining fiber optic cabling for the backbone and Cat6 for in-building connections may become more common, offering a balance between performance and cost.
In summary, both fiber optic and Cat6 cabling have their place in networking, with the choice depending on specific use cases, network speed needs, and budgets. Fiber optics excel in high-speed, long-distance, and critical applications, while Cat6 cabling remains practical for everyday networking needs. Monitoring emerging standards and trends is vital for making informed cabling decisions in the rapidly evolving networking landscape.
Conclusion
The networking landscape of 2023 presents myriad possibilities, with fiber optic cabling and Cat6 cabling as the brushstrokes of connectivity. Your choice between these two options is pivotal, shaping the efficiency and potential of your network.
As you stand at the crossroads of networking decisions in this dynamic year, remember that the future of your digital connectivity is in your hands. The call to action is clear: assess your network’s unique requirements, weigh the benefits and applications of fiber optic and Cat6 cabling, and make an informed decision that aligns with your aspirations. For further guidance and exploration of networking solutions, visit www.holightoptic.com or contact us at sales@holightoptic.com. Allow your network to flourish and thrive, embracing the possibilities that technology unveils in the digital age of 2023.