Satellite communication systems have been a cornerstone of global communication networks for decades, enabling reliable transmission of data across vast distances. However, with the exponential growth of data traffic, especially due to high-demand applications such as streaming, cloud services, and IoT, these systems face increasing pressure to deliver faster and more efficient communication. Optical fiber, renowned for its capacity to transmit large volumes of data at high speeds, plays a crucial role in modernizing satellite communication. This blog delves into how optical fiber is transforming satellite systems and looks at the future of this technological synergy.
1. The Key Role of Optical Fiber in Modern Communication

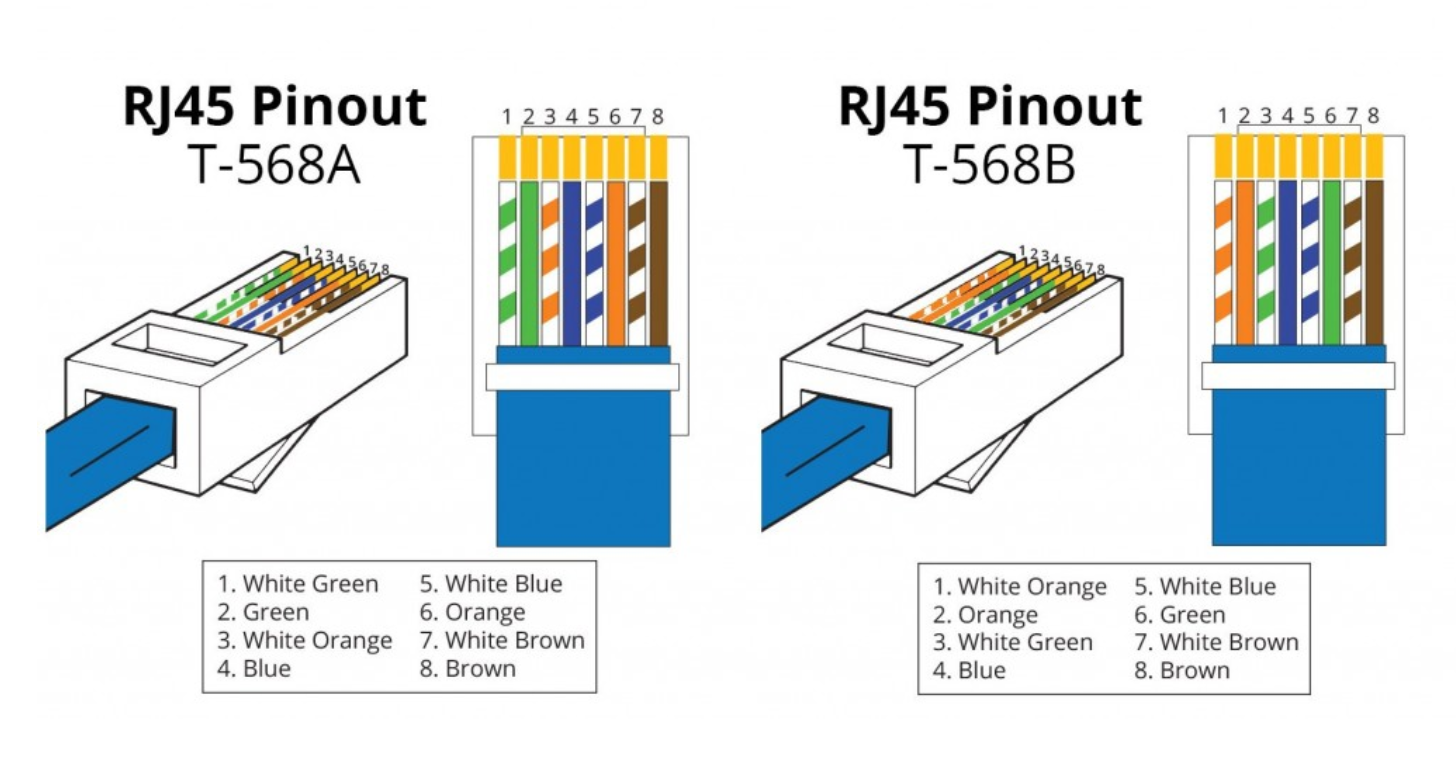
Optical fiber is fundamental to the global communications infrastructure due to its ability to transmit data as light signals over long distances with minimal signal degradation. Unlike traditional copper cables, which suffer from higher signal loss and interference, optical fiber offers a cleaner, faster, and more reliable means of data transmission. This advantage has made it indispensable for internet backbone systems, corporate networks, and telecommunication services.
Comparing Optical Fiber and Copper Cables:
| Feature | Optical Fiber | Copper Cable |
| Speed | Up to 100 Gbps | Up to 10 Gbps |
| Signal Degradation | Minimal over long distances | Significant over long distances |
| Bandwidth Capacity | Extremely high | Limited |
| Electromagnetic Interference | Resistant | Susceptible |
| Distance Coverage | Hundreds of kilometers without repeaters | Requires amplifiers every few kilometers |
In satellite communication, optical fiber serves as the primary link between ground stations and the broader terrestrial network, carrying vast amounts of data to and from satellites. For example, an undersea optical fiber cable can link two continents, transmitting data that is then uplinked to a satellite, which relays the signal to remote locations. By enabling high-speed data transfer to satellite stations, optical fiber is essential for reducing latency and improving the overall efficiency of satellite communications.
Moreover, as the demand for faster internet grows due to the rise of 5G and IoT, optical fiber’s role in satellite systems is becoming even more crucial. Its ability to handle high volumes of data ensures that satellite systems can keep up with the needs of modern industries.
2. How Optical Fiber and Satellite Communication Work Together

Satellite communication provides coverage over vast, remote areas where terrestrial networks may not reach. On the other hand, optical fiber networks form the backbone of global data transmission systems, connecting cities, data centers, and telecommunication hubs. Together, these technologies complement each other in a way that enhances the overall efficiency and reach of communication systems.
Satellite and Optical Fiber Communication Workflow:
- Data Transmission: Data generated by users is first transmitted via optical fiber to a satellite ground station.
- Uplink to Satellite: From the ground station, the data is then uplinked to a geostationary or low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite.
- Data Relay: The satellite receives and processes the data before relaying it to another satellite or ground station.
- Downlink via Fiber: The receiving ground station forwards the data through optical fiber to its final destination.
Illustrative Workflow of Data Transfer between Fiber and Satellite Communication:
The above workflow highlights how optical fiber allows seamless data movement between ground stations and satellites. One practical example is in underdeveloped regions, where laying fiber over rough terrain is challenging. In these cases, satellites provide a necessary communication link, while optical fiber ensures efficient data handling at the ground level. This coordination enables faster internet speeds, lower latency, and more robust communication systems.
The hybrid use of optical fiber and satellite also ensures that data can be transmitted reliably in adverse conditions. For instance, if bad weather affects satellite signal quality, fiber networks can help reroute the data, ensuring no disruption in services.
3. Enhancing Speed and Efficiency in Satellite Communication through Optical Fiber

One of the main advantages of optical fiber in satellite communication is the significant enhancement in data speed and transmission efficiency. Traditional satellite communications suffer from high latency, particularly when satellites are positioned far from Earth. Optical fiber, with its extremely fast transmission rates, helps offset this latency by ensuring rapid data transmission between ground stations and satellites.
Latency Comparison Between Satellite and Optical Fiber:
| Communication Method | Average Latency (ms) |
| Satellite (Geostationary) | 500-600 ms |
| Satellite (LEO) | 20-30 ms |
| Optical Fiber | < 5 ms |
By integrating optical fiber, satellite systems can significantly reduce the time it takes for data to travel from one point to another. For applications like live video conferencing, remote surgeries, or autonomous vehicle control, this reduction in latency is crucial. In these cases, even a few milliseconds of delay can affect the performance of the entire system.
Furthermore, the higher bandwidth capacity of optical fiber allows satellite systems to handle more data simultaneously, thus improving overall throughput. This is particularly beneficial for high-bandwidth applications such as high-definition video streaming, real-time analytics, and data-heavy IoT devices.
The efficiency of optical fiber doesn’t just stop at speed. It also supports higher transmission capacity by enabling wavelength division multiplexing (WDM), where multiple signals are transmitted over the same fiber using different wavelengths of light. This allows satellite systems to handle larger volumes of data without requiring additional physical infrastructure.
4. Challenges and Future Integration of Optical Fiber in Satellite Communication System

Although the integration of optical fiber in satellite communication systems presents many advantages, several challenges need to be addressed for its widespread adoption.
First, the cost of laying optical fiber networks, particularly in remote regions, can be prohibitively expensive. While satellites can cover vast areas with minimal ground infrastructure, building fiber networks across oceans, deserts, or mountainous regions requires significant investment. In such cases, satellite communication remains the more feasible option for providing connectivity.
Second, the technical complexity of synchronizing optical fiber networks with satellite systems also presents a challenge. Unlike satellites, which operate in space, optical fiber operates in terrestrial environments, and ensuring seamless data transfer between these two domains requires sophisticated technologies such as adaptive signal processing, dynamic routing, and advanced error-correction algorithms.
Challenges of Fiber and Satellite Integration:
| Challenge | Impact | Potential Solution |
| High cost of fiber deployment in remote areas | Limits fiber expansion | Use of satellite-based fiber hybrids |
| Synchronization of fiber and satellite signals | Risk of latency or signal loss | Adaptive signal processing |
| Evolving satellite technology (e.g., LEO constellations) | Need for advanced fiber capabilities | Multi-core fiber and WDM technologies |
In terms of future integration, ongoing advancements in optical fiber technology, such as multi-core fibers and quantum communication, will likely play a pivotal role in improving satellite communication systems. The development of LEO satellite constellations, which offer lower latency and higher capacity than traditional geostationary satellites, further underscores the need for advanced fiber networks that can support these new satellite systems.
At HOLIGHT, we specialize in the manufacturing and processing of high-quality optical fiber products. With a commitment to precision and quality, we supply the necessary building blocks that drive optical fiber networks worldwide. To learn more about our manufacturing services and products, visit www.holightoptic.com.